How to Make Buck Converter DIY Homemade Circuit Diagram Buck Converter Basic Function. Before going to buck converter design tutorial, we will discuss first how buck converter works in order to fully understand the following tutorial. A buck converter is a switching converter with a voltage output lower than voltage input. It is also called as a step-down switching converter

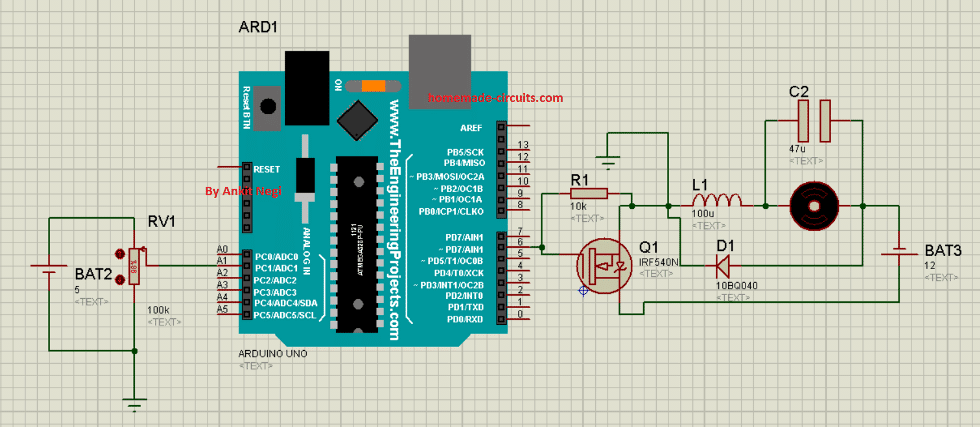
That's enough theory; now let's examine a straightforward real-world circuit. Making a Practical Buck Converter Design. The following figure shows a simple practical DC to DC buck converter circuit using only 3 transistors and a few other passive elements. It works in the following manner: Switch S in this circuit is represented by transistor T1.
Buck Converter Basics: Design, Operation, and Applications Circuit Diagram
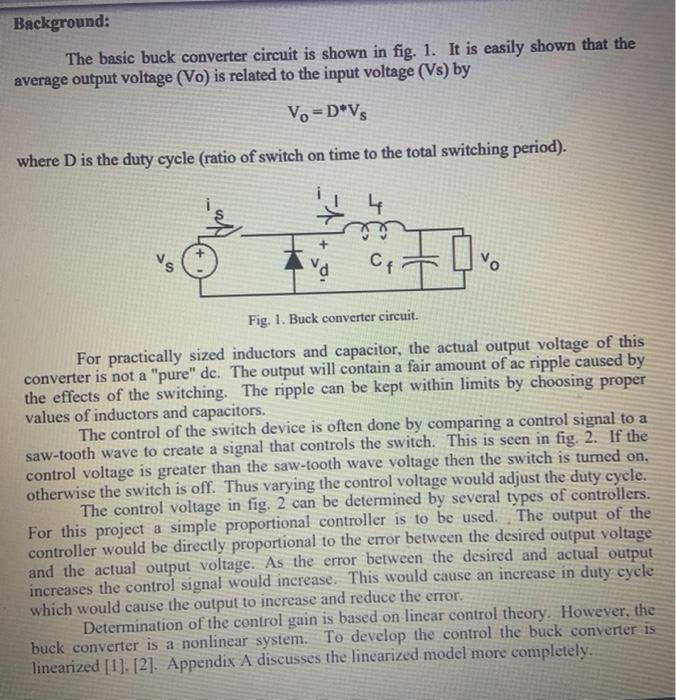
Circuit diagram of a buck converter. A basic buck converter comprises essential components like a switch (MOSFET or BJT), an inductor, a diode (or a second MOSFET), and a capacitor, as depicted in Fig 2. To design a buck converter, it is essential to determine the values of the capacitor, inductor, diode size, and switch size. The following The basic components of the switching circuit can be rearranged to form a step-down (buck) converter, a step-up (boost) converter, or an inverter (flyback). These designs are shown in Figures 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively, where Figures 3 and 4 are the same except for the transformer and the diode polarity.

The working principle of a Buck Converter involves the conversion of a higher voltage to a lower voltage through a series of switches, inductors, and capacitors. The basic operating principle of a Buck Converter is as follows: The input voltage is connected to a switch (usually a MOSFET), which is controlled by a control circuit.
Simple Buck Converter Circuits using Transistors Circuit Diagram
Therefore, the Buck converter is chosen as the design because it meets all of the specified criteria. Then, the basic circuit topology of the Buck converter, which includes five standard components: (1) a pulse-width modulating controller, (ii) a switch, (iii) an inductor, (iv) a capacitor, and (v) a diode.
