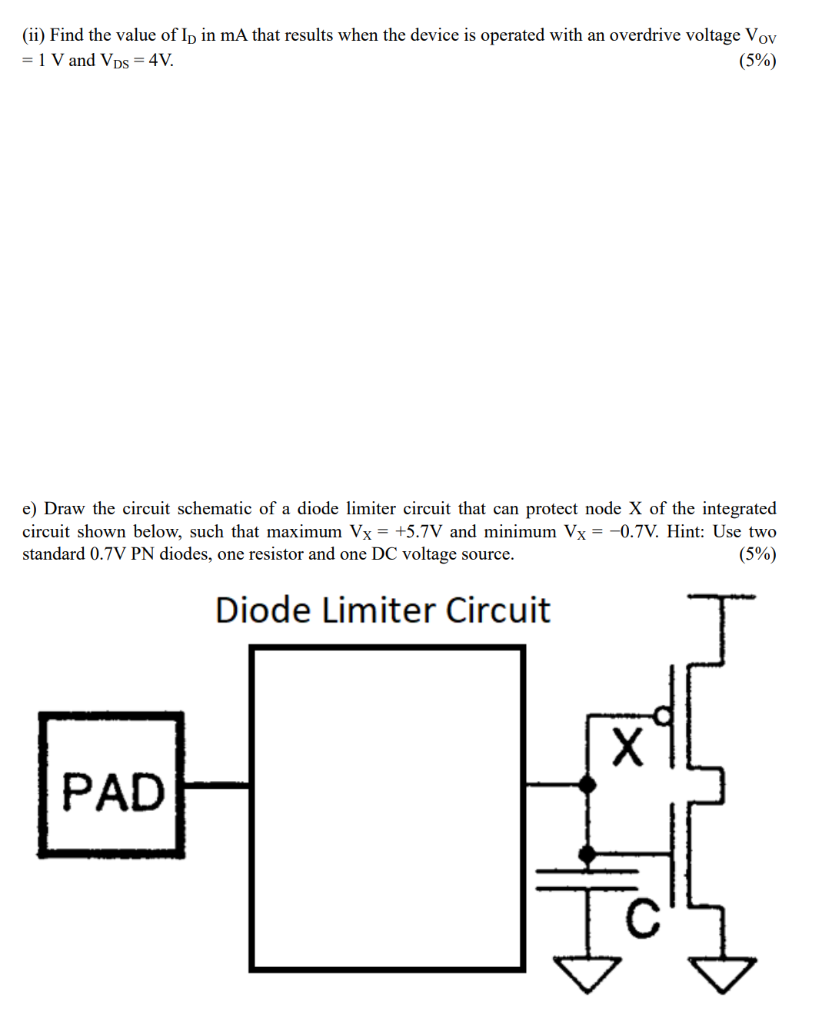
Transistor Amplifier circuit to generate regulated output Circuit Diagram Transistor Amplifier P1 A simple explanation of how a transistor works in a circuit, and how to connect transistors to create a number of different circuits. No mathematics and no complex wording. Just a completely different approach you can understand . . . TOPICS: Adjustable Current Power Supply Adjusting The Stage Gain AF Detector

An amplifier circuit which is purely based on a transistor or transistors is called a transistor amplifier. Transistors amplifiers are commonly used in applications like RF (radio frequency), audio, OFC (optic fibre communication) etc. Anyway the most common application we see in our day to day life is the usage of transistor as an audio amplifier. In this case if we applied the input signal of 0 degree phase then output will be obesrved to be Phase of 180 degree. The common-emitter amplifier design is called an inverting amplifier. Examples. Q1. The output resistance of a common base transistor amplifier is 100 kΩ, while the input resistance is 10 Ω. One kΩ is the collector load.
PDF Section 3: BJT Amplifiers Circuit Diagram
K. Webb ECE 322 4 BJT Amplifier Circuits Recall the two functional pieces of a BJT amplifier: Bias network Sets the DC operating point of the transistor Ensures the BJT remains in the forward-active region Signal path Biasing. Network Signal path Sets the gain of the amplifier circuit Significant overlap between the two parts The single transistor amplifier is one of the major keys to understanding the analysis and design of all analog electronic systems. Stereos, television sets, radios, long distance telephone communication circuits, and many other practical systems employ principles that we will explore in this experiment.
The choice of the transistor depends on the frequency range and the power level. Here, we are making a small signal AF amplifier and can use any of the hundreds of transistors. So let's use the well-known BC337. How the circuit works. Our design begins with a look inside the transistor itself. The Base of the transistor used in a common emitter amplifier is biased using two resistors as a potential divider network. This type of biasing arrangement is commonly used in the design of bipolar transistor amplifier circuits and greatly reduces the effects of varying Beta, ( β) by holding the Base bias at a constant steady voltage. This

Transistor As An Amplifier Circuit Diagram
Students will learn to design, assembly and determine the behavior of electronic devices and circuits that use resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, transistors and operational amplifiers. Successful completion of this lab will help students to demonstrate (1) understanding of electrical circuits in practical applications, (2) ability to
